Glaucoma is often called the “silent thief of sight” because it can develop slowly and without noticeable symptoms in its early stages. This makes it a particularly dangerous eye condition, as many people may not realize they have it until significant damage has already occurred.
Understanding the early signs of glaucoma is crucial for preserving your vision and overall eye health. Keep reading to learn about the first signs of glaucoma and how to protect your eyesight!
What is Glaucoma?
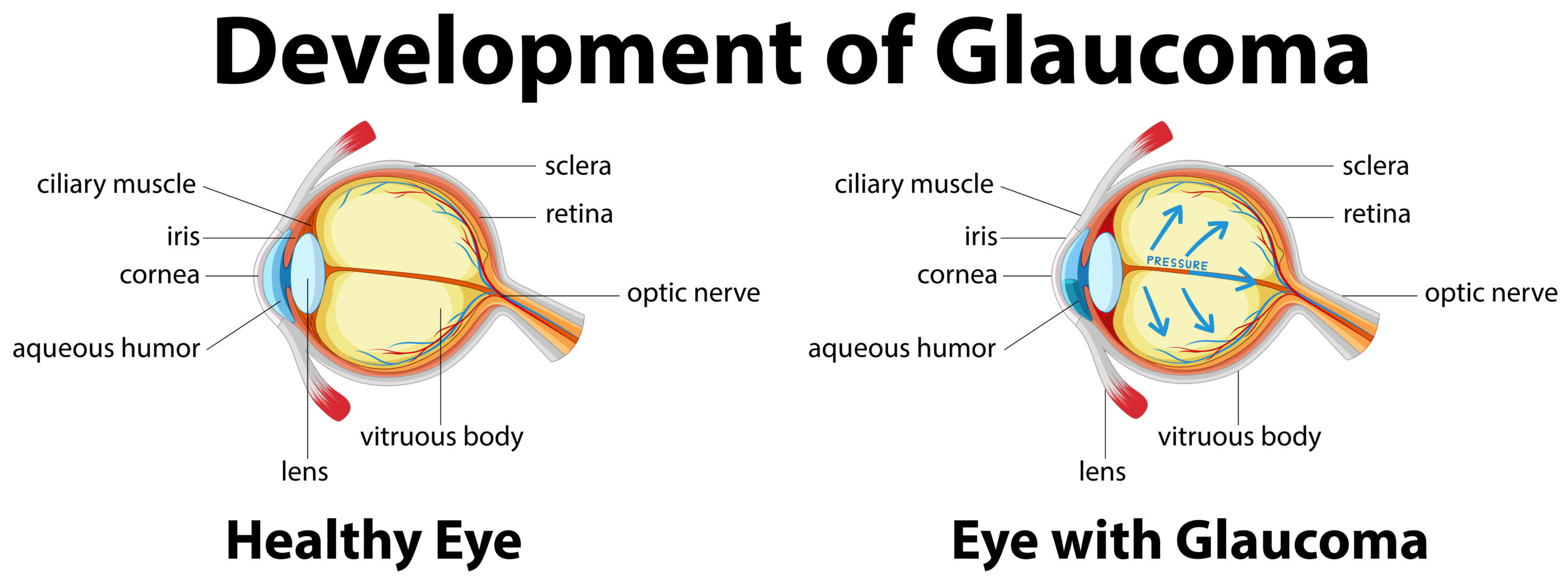
Glaucoma is a group of eye conditions that damage the optic nerve. The optic nerve is an essential part of the eye, as it is responsible for transmitting visual information from your eyes to your brain.
This damage that occurs with glaucoma is often associated with increased pressure within the eye, known as intraocular pressure (IOP). However, it’s important to note that not all cases of glaucoma involve high eye pressure. There are several types of glaucoma.
Two important ones to know about are open-angle glaucoma and angle-closure glaucoma. Open-angle glaucoma is the most common form of glaucoma.
It typically develops gradually over time. Angle-closure glaucoma, on the other hand, often happens suddenly, causing many symptoms, and is considered a medical emergency.
Glaucoma can affect people of all ages, but it becomes more common as we get older. If left untreated, glaucoma can lead to progressive vision loss and, ultimately, blindness.
This is why early detection is crucial in managing the condition and preserving vision.
How Do I Know If I Have Glaucoma?
Detecting glaucoma in its early stages can be challenging because the condition often develops without noticeable symptoms. This is why regular comprehensive eye exams are crucial for early detection and management of glaucoma.
During a comprehensive eye exam, your eye doctor at Blaine Eye Clinic will perform several tests to check for glaucoma. This will include eye pressure testing and a thorough examination of your optic nerve.
These tests can help detect glaucoma even before you experience any vision changes. For most adults, an eye exam every one to two years is recommended.
However, if you have risk factors for glaucoma or are over the age of 60, your eye doctor may suggest more frequent examinations.
What is the First Symptom of Glaucoma?
The first detectable symptom of the most common form of glaucoma, open-angle glaucoma, is often a gradual loss of peripheral (side) vision. This can be difficult to notice at first, as your brain may compensate for the loss by filling in the gaps.
You might find yourself bumping into objects on the side or having trouble seeing things out of the corner of your eye. However, it’s crucial to understand that by the time you notice vision changes, significant damage may have already occurred.
This is why glaucoma is often detected during routine eye exams before any symptoms are apparent. For angle-closure glaucoma, which develops rapidly, the first symptoms can be more sudden and severe.

These may include:
- Severe eye pain
- Headache
- Nausea and vomiting
- Blurred vision
- Halos around lights
- Redness of the eye
If you experience these symptoms, it’s important to seek immediate medical attention, as angle-closure glaucoma is considered an emergency.
Does Glaucoma Cause Pain?
In most cases, particularly with open-angle glaucoma, there is no pain associated with the condition in its early stages. This lack of discomfort is one reason why glaucoma can progress unnoticed for a long time.
However, angle-closure glaucoma, which occurs when the iris blocks the drainage angle in the eye, can cause severe pain. This pain is often described as an intense, throbbing ache in or around the eye.
It may be accompanied by headaches, nausea, and vomiting. Some people with normal-tension glaucoma may experience discomfort or a feeling of pressure around the eyes, but this is not typically described as pain.
It’s important to remember that the absence of pain does not mean an absence of the condition. Regular eye exams are the best way to detect glaucoma before it causes noticeable symptoms or discomfort.
Can You Prevent Glaucoma From Damaging Vision?
While not all cases of glaucoma can be prevented, there are several steps you can take to reduce your risk and protect your vision:

Regular Eye Exams
Schedule comprehensive eye exams as recommended by your optometrist. Early detection is key to preventing vision loss from glaucoma.
Know Your Family History
If you have a family history of glaucoma, share this information with your eye care provider. You may need more frequent screenings.
Protect Your Eyes
Wear protective eyewear during sports or when working with tools to prevent eye injuries that could lead to glaucoma.
Manage Chronic Health Conditions
If you have diabetes, high blood pressure, or other chronic health conditions, work with your healthcare providers to keep these under control.
Use Prescribed Eye Drops
If you’ve been diagnosed with high eye pressure or early-stage glaucoma, use any prescribed eye drops consistently as directed by your eye doctor.
Protect Your Eyes From Glaucoma
Remember, while these steps can help reduce your risk, they cannot guarantee glaucoma prevention. Regular eye exams remain the most effective way to detect and manage glaucoma early.
At Blaine Eye Clinic, our experienced eye doctors are equipped to detect glaucoma in its earliest stages and provide appropriate treatment or referrals when necessary. Don’t wait for symptoms to appear before scheduling an eye exam.
Early detection is key in managing glaucoma and preventing vision loss.
Are you experiencing symptoms of glaucoma? Schedule an appointment at Blaine Eye Clinic in Blaine, MN, today!





