If you are one of the many people all over the world with diabetes, regular diabetic eye exams are crucial for protecting your vision and overall health. High blood sugar levels associated with diabetes can damage the blood vessels in the retina at the back of the eye, leading to diabetic retinopathy and other complications that may cause permanent vision loss.
Keep reading to learn more about diabetic eye disease and what happens during a diabetic eye health exam!
How Can Diabetes Affect The Eyes?

Over time, uncontrolled blood sugar from diabetes can cause damage to the eye in multiple ways. High glucose levels can lead to blockages in the tiny retinal blood vessels, preventing oxygen from reaching the retina.
This oxygen deprivation starves delicate retinal tissue, killing the cells. In response, the retina attempts to grow fragile new blood vessels.
However, these abnormal vessels are prone to swelling and bleeding, allowing fluid to leak into the retinal tissue, which damages your vision. This growth of weak blood vessels typically characterizes diabetic retinopathy, which is the most common diabetic eye disease.
On top of diabetic retinopathy, persistent high blood sugar levels also make diabetics more likely to develop cataracts, glaucoma, corneal issues, and loss of peripheral vision. Nearly all people with diabetes will experience at least some eye complications if their blood sugar control is poor.
Without intervention, diabetic eye disease can progressively lead to severe vision loss or blindness. For this reason, it is important for those with diabetes to visit their eye doctor routinely to ensure they are not at risk of vision loss.
What Are the Symptoms of Diabetic Eye Disease?
Since there are many different eye conditions that can be caused or worsened by diabetic eye disease, there are also many symptoms. Diabetic retinopathy, the most common eye condition associated with diabetes, has different stages that can present different symptoms.
As the eye condition progresses, symptoms may include:
- Blurry or constantly fluctuating vision
- Dark or empty spots in vision
- Vision loss
- Eye pain or redness
If you notice any changes in your vision, it is essential to visit your eye doctor for an examination. This is why routine diabetic eye exams are so important for detection before complications escalate.
What Happens During a Diabetic Eye Health Exam?
A diabetic eye exam is very similar to a routine eye check-up, with a few added tests specifically to inspect blood vessels in the eyes. The key elements of the exam include:
Visual Acuity Assessment
The visual acuity assessment checks how clearly you can see. You will read letters or look at an eye chart from a standard distance.
This tests your central and reading vision abilities, which are crucial for daily tasks. It helps diagnose refractive errors and other focus issues.
Tracking changes over time shows if vision is stable or declining.
Dilating Eye Drops to Open the Pupil Wide
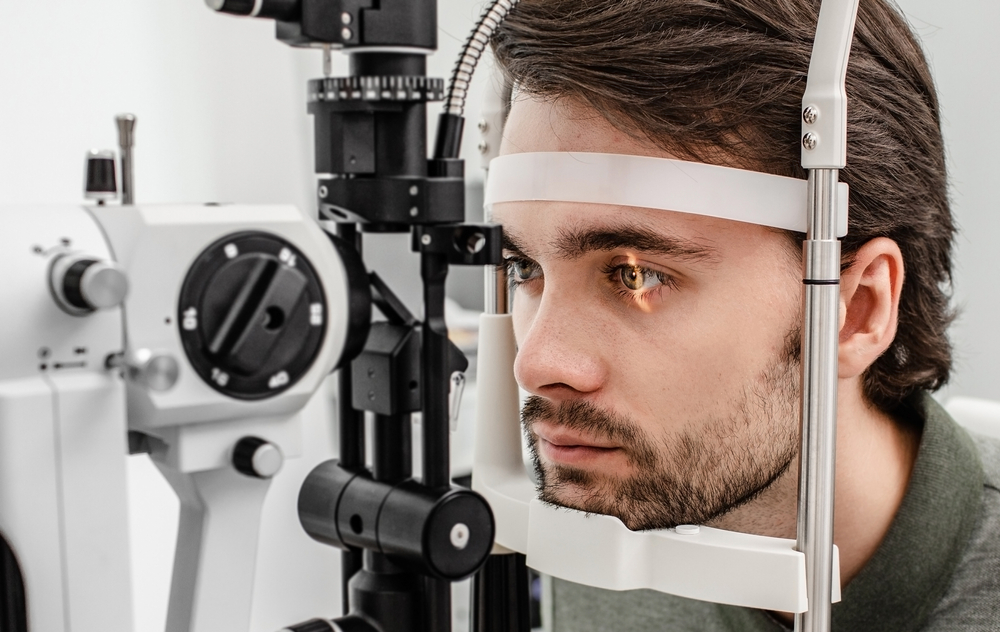
Dilating drops widen the pupil to allow more light into the eye for better visibility for your eye doctor. Drops temporarily paralyze the iris, so the pupil remains big.
This allows your optometrist to get a very thorough look inside the entire eye, especially the retina. It makes tiny details clearer that might be obscured if the pupil were small.
Dilated exams are key for evaluating the retina for signs of diabetic damage to the blood vessels and retinal tissue.
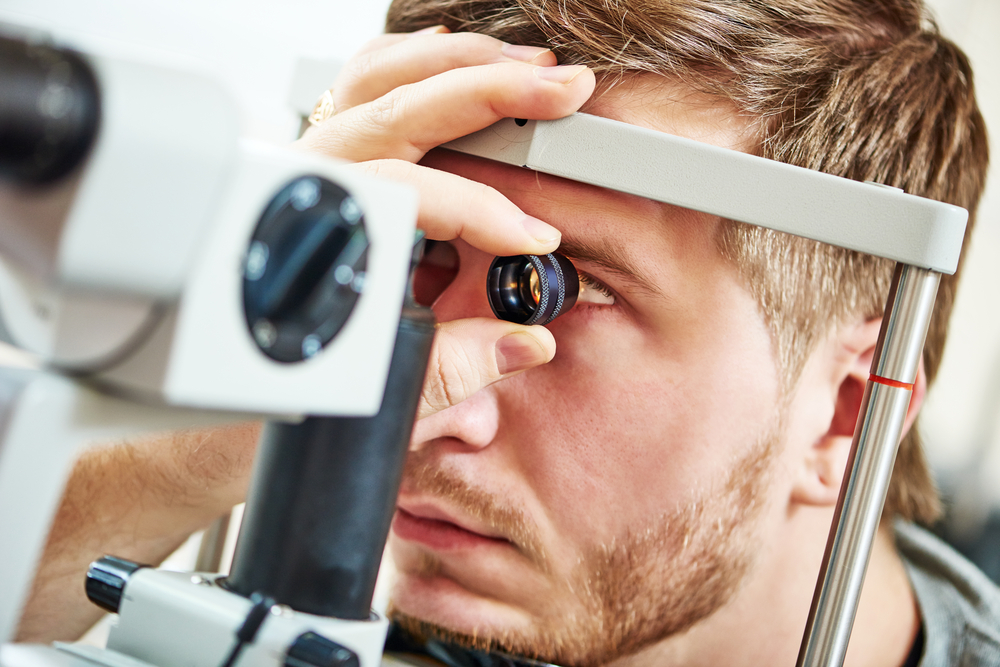
Close Inspection of the Retina and Blood Vessels
A technique called slit lamp microscopy with bright illumination and magnification is used to closely inspect the retina and blood vessels while the pupil is wide. Signs like leaking fluid and blood, swelling, abnormal blood vessel growth, and retinal tissue damage can indicate diabetic retinopathy.
Your optometrist will look for any retina changes from previous exams that need monitoring or treatment.
Additional Tests as Needed
Other imaging, scans, and tests may be warranted if the optometrist spots potential issues. These provide expanded views, detailed photos, and depth analysis of the retina and structures inside the eye to assess for diabetic complications.
Test results are compared over time to help your eye doctor understand if the condition is worsening and if/when treatment is required.
At Blaine Eye Clinic, our optometrists will explain all results and next steps before you leave your appointment. If you are diagnosed with diabetic retinopathy, they will determine whether or not you need to be referred to a specialist.
How Often Do I Need to Have My Eyes Checked if I am Diabetic?
 The American Optometric Association recommends that people with diabetes receive a full dilated eye exam annually. Pregnant women with diabetes or diabetics experiencing vision changes should be examined more frequently.
The American Optometric Association recommends that people with diabetes receive a full dilated eye exam annually. Pregnant women with diabetes or diabetics experiencing vision changes should be examined more frequently.
However, your primary care doctor, endocrinologist, or eye doctor may have other specific recommendations for you. It is important to follow their recommendations to ensure that your vision and eyes are protected.
Early detection and treatment monitoring are essential to preserve vision with diabetes. Routine diabetic eye health checks allow our optometrists at Blaine Eye Clinic to monitor changes and detect issues before complications arise.
If you are diabetic, schedule your next exam today. Protecting your vision starts with understanding and monitoring the health of your eyes.
Is it time for you to have a diabetic eye exam? Schedule an appointment at Blaine Eye Clinic in Blaine, MN, today!





